Influenza (the flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild to severe illness, and at times can lead to death. Some people, such as older people, young children, and people with certain health conditions, are at high risk for serious flu complications. The best way to prevent the flu is by getting vaccinated each year.
MRSA is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a potentially dangerous type of staph bacteria that is resistant to certain antibiotics and may cause skin and other infections. You can get MRSA through direct contact with an infected person or by sharing personal items, such as towels or razors that have touched infected skin.
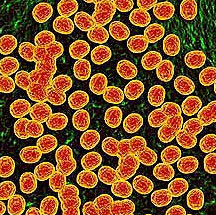
Salmonellosis is an infection with bacteria called Salmonella. Salmonella germs have been known to cause illness for over 100 years. Most persons infected with Salmonella develop diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps 12 to 72 hours after infection. The illness usually lasts 4 to 7 days, and most persons recover without treatment.
Escherichia coli (abbreviated as E. coli) are a large and diverse group of bacteria. Although most strains of E. coli are harmless, others can make you sick. Some kinds of E. coli can cause diarrhea, while others cause urinary tract infections, respiratory illness and pneumonia, and other illnesses.
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver and also refers to a group of viral infections that affect the liver . The most common types are Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C.
Viral hepatitis is the leading cause of liver cancer and the most common reason for liver transplantation.
Human scabies is caused by an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies.
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash caused by the varicella zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. Nearly 1 out of every 3 people in the United States will develop shingles. Anyone who has recovered from chickenpox may develop shingles; even children can get shingles. However, the risk of getting the disease increases as a person gets older.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a potentially serious illness. Experts believe WNV is established as a seasonal epidemic in North America that flares up in the summer and continues into the fall. WNV is a flavivirus commonly found in Africa, West Asia, and the Middle East. It is closely related to St. Louis encephalitis virus which is also found in the United States. The virus can infect humans, birds, mosquitoes, horses and some other mammals.
Eastern Equine Encephalitis is a rare disease that is caused by a virus spread by infected mosquitoes. Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus (EEEV) is one of a group of mosquito-transmitted viruses that can cause inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). In the United States, approximately 5-10 Eastern Equine Encephalitis cases are reported annually. Eastern Equine Encephalitis is a rare illness in humans, and only a few cases are reported in the United States each year.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain. If not treated properly, TB disease can be fatal. TB disease was once the leading cause of death in the United States.
The rabies virus is transmitted through saliva or brain/nervous system tissue. You can only get rabies by coming in contact with these specific bodily excretions and tissues. It's important to remember that rabies is a medical urgency but not an emergency. Decisions should not be delayed.
Meningitis is a disease caused by the inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord known as the meninges. The inflammation is usually caused by an infection of the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis may develop in response to a number of causes, usually bacteria or viruses, but meningitis can also be caused by physical injury, cancer or certain drugs.